
The break-even point (BEP) is a key financial measure that defines the point at which the total revenue of a hotel or restaurant covers the total costs without making a profit or loss. This indicator is of great importance in the hotel and catering industry, as these sectors are characterized by high fixed costs and variable sales that are strongly influenced by seasonal fluctuations and customer behaviour. Knowledge of the BEP helps operators to adjust their prices, budgets and operational processes to ensure profitability, especially in the crucial start-up phase.
The BEP is calculated using the following formula:
Break-even sales = fixed costs / price per unit – variable costs per unit
Fixed costs include all regular expenses such as rent, salaries and insurance that are not directly influenced by sales. Variable costs change depending on the number of guests or units sold and include items such as food costs in restaurants or cleaning costs in hotels. The price per unit reflects the average sales price per overnight stay or dish.
Revenue is generated with every sale of goods or services. However, the BEP shows the point at which sales are sufficient to fully cover costs and thus achieve economic equilibrium. Beyond this point, every product or service sold contributes to profit.
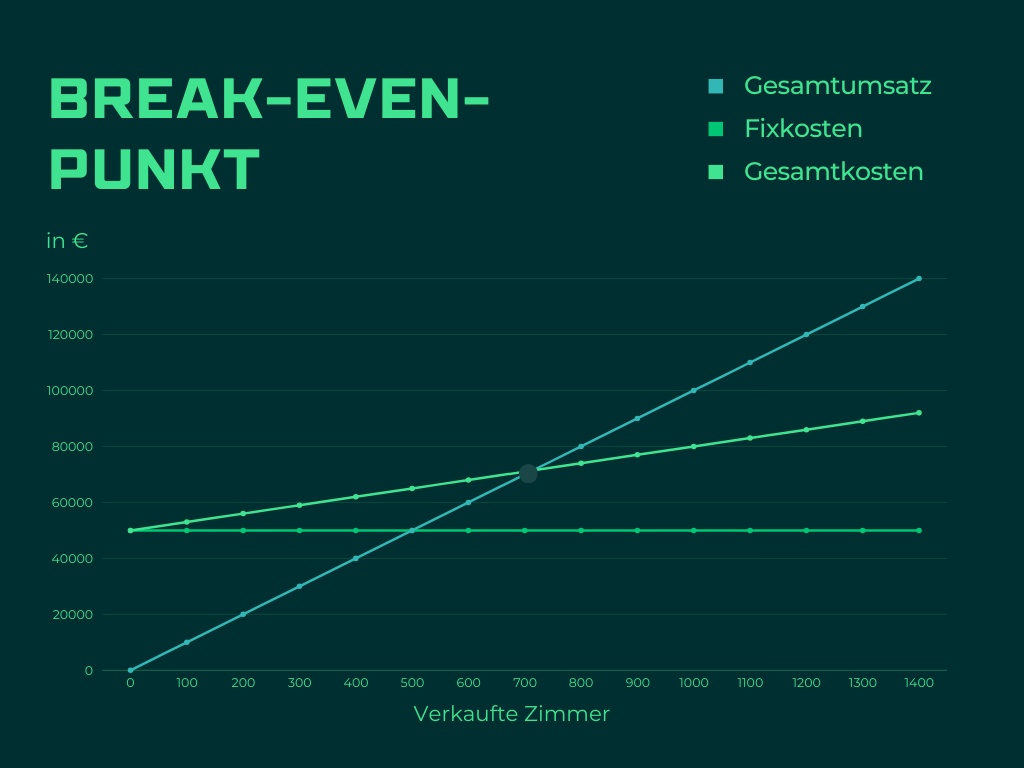
A hotel with monthly fixed costs of EUR 50,000 and a price of EUR 100 per room per night with variable costs of EUR 30 per room per night achieves the BEP with 714 room nights sold per month. Every additional room sold increases the profit.
Graphically, it is as follows:
The fixed costs are constant and do not change with the quantity sold. The variable costs increase with the number of rooms sold. Total revenue also increases with the number of rooms sold.
The sectors are susceptible to fluctuations in demand due to tourism trends and seasonal events. A precise understanding of BEP enables operators to respond effectively to such fluctuations, plan prices and capacities strategically and minimize risks.